A laser engraving machine is a cutting-edge tool that uses laser technology to etch precise designs, patterns, or text onto various materials. It has revolutionized industries ranging from manufacturing and art to education and small businesses by offering unparalleled precision and efficiency. These machines leverage advanced technology to work seamlessly on materials like wood, metal, acrylic, leather, and more, enabling endless creative and industrial possibilities. With the growing demand for customization and innovation, laser engraving machines are becoming indispensable tools, driving advancements in productivity and creativity. Read Out!
How Laser Engraving Machines Work?
Laser engraving involves using a focused beam of light to remove material from the surface of an object. The laser beam, directed by a highly precise system, vaporizes the material in specific patterns, leaving behind a permanent mark. This process is contactless, ensuring clean and detailed results without damaging surrounding areas. The engraving depth and design are controlled by the laser’s power, speed, and focus.
Components of a Laser Engraving Machine
- Laser Source
The laser source generates the intense light beam used for engraving. Different types of laser sources, such as CO2, fibre, or diode lasers, are chosen based on the material and application. The laser’s wavelength and power determine its effectiveness on various surfaces.
- Controller
The controller acts as the brain of the engraving machine, interpreting design files (e.g., from CAD or vector software) and directing the laser’s movements. It controls factors like speed, power, and positioning, ensuring precise execution of designs.
- Engraving Surface/Bed
The engraving bed holds the material securely in place. It is often adjustable to accommodate varying material sizes and thicknesses. Some machines feature honeycomb beds or rotary attachments for engraving irregular shapes, like cylindrical objects.
Types of Laser Engraving Processes
- Vector Engraving
Vector engraving involves laser tracing of the outline of a design, such as lines and curves. It is commonly used for text, logos, and intricate line art. The laser follows a continuous path, similar to a pen drawing on paper.
- Raster Engraving
Raster engraving works by scanning the laser back and forth, similar to how a printer works, creating detailed images or filled areas. This technique is ideal for photographs, patterns, and other complex designs requiring shading and texture.
Materials Compatible with Laser Engraving
Laser engraving machines are versatile tools that work on a wide variety of materials. Popular options include:
- Wood: Common for signs, decorations, and personalized items.
- Metal: Used in industrial applications, jewellery, and tool marking.
- Acrylic: Perfect for creating vibrant signs and artistic designs.
- Leather: Engraves custom patterns and logos on wallets, bags, and belts.
- Glass: Ideal for etching logos or designs on bottles, trophies, and glassware.
- Plastic: Used in electronics and nameplates.
The adaptability of laser engraving machines to various materials makes them indispensable in industries ranging from manufacturing to arts and crafts.
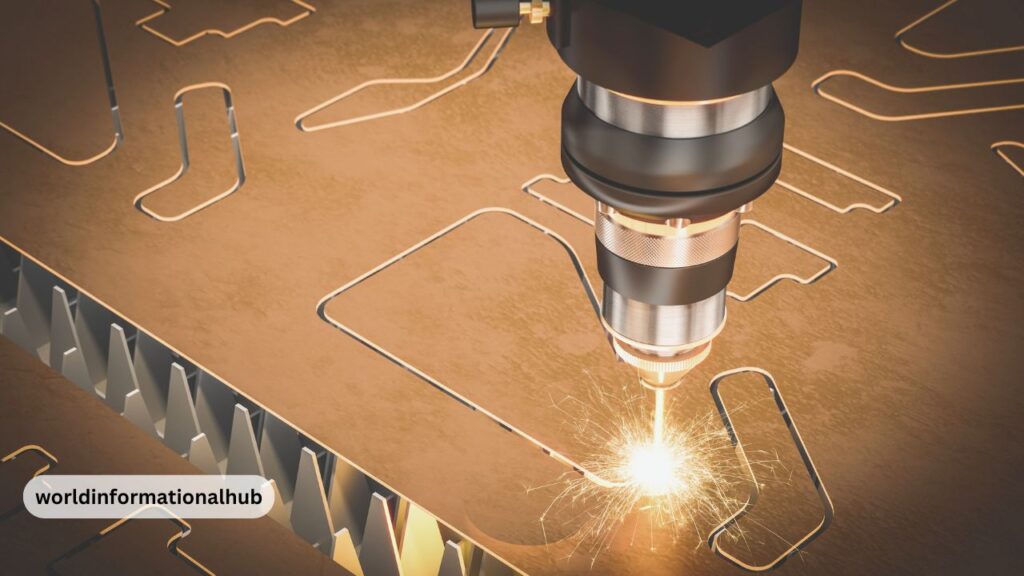
Types of Laser Engraving Machines
Laser engraving machines come in different types, each designed for specific applications and materials.
| Machine Type | Best For | Key Features | Cost |
| CO2 Laser | Non-metals (wood, acrylic, leather) | High-speed, versatile, affordable | Medium |
| Fiber Laser | Metals (steel, brass, aluminium) | Precision, durability, industrial use | High |
| Diode Laser | Small projects, wood, paper | Portable, beginner-friendly | Low |
| UV Laser | Glass, ceramics, delicate materials | Cold engraving, minimal heat damage | High |
Here is a breakdown of the most commonly used types of laser engraving machines:
1. CO2 Laser Engraving Machines
CO2 laser engraving machines are among the most commonly used types, utilizing carbon dioxide gas as the laser source. These machines are highly versatile and capable of engraving non-metallic materials such as wood, glass, acrylic, leather, and certain plastics. CO2 lasers are known for their precision and affordability, making them popular for creative industries, small businesses, and artisans. They are ideal for detailed designs and customization projects, but they typically require higher power levels to engrave harder materials like stone or coated metals.
2. Fiber Laser Engraving Machines
Fibre lasers are specialized tools designed for marking and engraving metals and certain plastics. They use fibre-optic cables to amplify the laser beam, producing high-intensity light with exceptional accuracy. These machines are widely used in industrial applications, such as marking serial numbers, barcodes, and logos on tools, automotive parts, and medical devices. Fibre lasers are low-maintenance and energy-efficient, offering faster engraving speeds compared to other types. However, they are less suitable for non-metallic materials like wood or glass.
3. Diode Laser Engraving Machines
Diode laser engraving machines are compact and budget-friendly, making them a popular choice for hobbyists and small-scale projects. They use a semiconductor-based laser source, which is ideal for engraving soft materials like wood, leather, and certain plastics. While these machines are not as powerful as CO2 or fibre lasers, they are easy to operate and portable, making them perfect for DIY enthusiasts and beginners. The primary limitation of diode lasers is their inability to effectively engrave metals or other hard materials.
4. UV Laser Engraving Machines
UV laser engraving machines use ultraviolet light with a shorter wavelength, allowing for extremely fine and precise engraving. This makes them ideal for delicate materials like glass, crystals, ceramics, and certain plastics, where precision and minimal heat impact are crucial. These machines are commonly used in high-end industries such as electronics, medical devices, and luxury goods. Although UV lasers are versatile and effective, their high cost often restricts their use to specialized applications.
Features of Modern Laser Engraving Machines
Modern laser engraving machines are equipped with advanced features that enhance their precision, efficiency, and user-friendliness. These innovations make them indispensable tools across various industries. Below are the key features that define contemporary laser engraving machines:
Precision and Accuracy
One of the standout features of modern laser engraving machines is their exceptional precision. They can create intricate designs, text, and patterns with unparalleled accuracy, down to fractions of a millimetre. This precision ensures consistent results, whether engraving delicate jewellery or intricate industrial components.
Speed and Efficiency
Advanced laser engraving machines are designed for high-speed operation without compromising quality. With adjustable speed settings, users can optimize the engraving process based on the material and design complexity. Faster operation translates to increased productivity, especially in mass production settings.
Software Compatibility
Modern machines are compatible with a wide range of software, including CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and vector-based tools like CorelDRAW, Adobe Illustrator, and AutoCAD. This compatibility allows users to create detailed designs digitally and seamlessly transfer them to the engraving machine. Some machines also come with proprietary software that simplifies the engraving process.
Portability and Compact Design
Portability is a key consideration for many users, particularly small business owners and hobbyists. Compact laser engraving machines are easy to transport and set up in limited spaces. Despite their smaller size, these machines often retain the performance capabilities of larger models, making them highly versatile.
Safety Features
Safety is a priority in modern laser engraving machines. Many models include features such as:
- Protective Enclosures: Shield users from laser exposure.
- Automatic Shutdown: Ensures the machine powers down if an issue is detected.
- Ventilation Systems: Remove fumes and debris generated during engraving. These features reduce risks and ensure compliance with safety standards, especially in industrial settings.
Ease of Use
Contemporary laser engraving machines are designed with user-friendly interfaces and intuitive controls. Touchscreen panels, pre-programmed settings, and guided tutorials make these machines accessible even to beginners. Features like autofocus and material recognition further simplify the engraving process.
Versatility in Material Handling
Modern machines can handle a wide variety of materials, from wood and metal to acrylic, glass, and leather. Some models include specialized attachments, like rotary devices for cylindrical objects or honeycomb beds for irregularly shaped materials. This adaptability broadens the scope of applications.
Customizable Power and Settings
Users can fine-tune the laser’s power, speed, and focus to suit specific materials and designs. For example, delicate materials like glass require lower power settings to prevent damage, while metals may require higher intensity. This level of control ensures optimal results for every project.
Connectivity Options
Advanced laser engraving machines often feature wireless connectivity, USB ports, and cloud-based integration. These options make it easy to upload designs, monitor progress remotely, and update software as needed. This connectivity streamlines the workflow and enhances flexibility.
Low Maintenance Requirements
Many modern machines are built with durability in mind, featuring self-cleaning mechanisms, long-lasting laser tubes, and robust construction. Regular software updates and minimal hardware maintenance ensure reliable performance over time.

Applications of Laser Engraving Machines
Laser engraving machines are incredibly versatile tools, finding applications across a wide array of industries. Their ability to etch precise, permanent designs on diverse materials makes them indispensable for both commercial and creative pursuits. Here are some key applications:
1. Industrial Use
- Manufacturing and Mass Production: Laser engraving machines play a pivotal role in manufacturing processes, especially for creating detailed markings like serial numbers, QR codes, and barcodes. These markings are essential for product identification, tracking, and compliance in sectors like electronics, automotive, and aerospace industries.
- Automotive and Aerospace Industries: In these sectors, laser engraving is used to mark parts, tools, and components to ensure traceability and meet strict safety regulations. The precision of laser technology is crucial for engraving high-resolution labels on small or irregularly shaped parts.
2. Artisan and Small Business Use
- JJewelleryDesign: Laser engraving machines are widely used to create intricate patterns, logos, and personalized messages on jjewellery Their precision ensures flawless designs on delicate items like rings, pendants, and bracelets.
- Personalized Gifts and Items: Small businesses and entrepreneurs utilize laser engraving to offer custom-made gifts such as engraved photo frames, plaques, keychains, and decorative items. This capability drives the demand for personalized, one-of-a-kind products.
3. Educational and Research Use
- Prototyping: Laser engraving machines aid in creating prototypes for projects in academic and research institutions. Students and researchers use these machines to precisely engrave or cut parts required for experiments, models, or presentations.
- Academic Projects: Educational institutions use laser engravers in their maker spaces or workshops to teach students about fabrication, design, and manufacturing processes.
4. Creative Use
- Home Décor: Artists and decorators employ laser engraving to craft unique home decor items such as engraved wall art, coasters, and ornaments. The precision allows for detailed designs that enhance aesthetic appeal.
- Art and Sculpture: Laser engraving serves as a valuable tool for artists who require precise etching on unconventional materials like wood, acrylic, or metal. This technique adds an extra dimension of creativity to sculptures and art installations.
5. Other Applications
- Medical Tools Engraving: In the medical industry, laser engraving is used to mark surgical tools and medical equipment with identification codes, ensuring traceability and hygiene compliance.
- Identification and Security Labeling: Laser engraving machines are employed to create permanent security markings on items like locks, nameplates, and ID cards. These markings are tamper-proof and withstand wear and tear, making them ideal for security purposes.
The adaptability of laser engraving machines to various industries and use cases demonstrates their growing importance. Whether it’s for mass production, artistic expression, or educational purposes, these machines are redefining the boundaries of precision and creativity.
Conclusion
Laser engraving machines have emerged as transformative tools, blending precision, efficiency, and versatility across a multitude of applications. From industrial manufacturing to creative artistry, these machines are empowering professionals, artisans, and businesses to achieve results that were once considered unattainable. Their ability to work seamlessly with a wide range of materials and their adaptability to various use cases underscore their indispensable role in modern technology.
As advancements in laser technology continue to unfold, we can expect further innovation, such as enhanced automation, AI integration, and broader material compatibility. These developments will make laser engraving more accessible, efficient, and capable of meeting the evolving demands of industries and individuals alike.
Whether you’re looking to streamline production, create personalized designs, or explore innovative craftsmanship, laser engraving machines offer endless opportunities. Their enduring value lies in their capacity to combine functionality and creativity, marking them as a cornerstone of precision technology in the modern era.
